Bronchiolitis: Brief Version
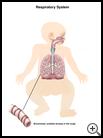
What is bronchiolitis?
Children most often get this disease between 6 months and 2 years of age. If your child has bronchiolitis:
- Your child may wheeze (make a high-pitched whistling sound when breathing).
- Your child may breathe rapidly (over 40 breaths per minute).
- Your child may have a cough and cough up a very sticky mucus.
A virus narrows the small airways of the lungs (the bronchioles.) This causes your child to wheeze. Your child may get an ear infection too. A few children may need to stay in the hospital.
How can I take care of my child?
- It may help to give your child asthma-type medicine. About 1/4 of children with bronchiolitis are helped by asthma medicines. Your healthcare provider may prescribe medicine for your child. Keep up with the medicine until your child does not wheeze for 24 hours. If your child has a high fever, give acetaminophen (Tylenol) every 4 to 6 hours or ibuprofen (Advil) every 6 to 8 hours.
- Use a humidifier. Moist air can help. Dry air tends to make coughs worse.
- Make sure your child's nose is not blocked up. If the nose is blocked up, your child will not be able to drink from a bottle or breast-feed. Put 3 drops of saline in each nostril. After about 1 minute, use a soft rubber suction bulb to suck out the mucus. You can buy saline nose drops at the drugstore. You don’t need a prescription.
- Make sure your child drinks enough fluids.
Call your child's doctor right away if:
- Your child has a hard time breathing.
- The wheezing gets very bad.
- Your child is breathing faster than 60 breaths per minute.
- Your child is acting very sick.
Call your child's doctor within 24 hours if:
- Any fever lasts more than 3 days.
- You have any other questions or concerns.
Written by Barton D. Schmitt, MD, author of “My Child Is Sick,” American Academy of Pediatrics Books.
Pediatric Advisor 2018.1 published by Change Healthcare.
Last modified: 2016-06-01
Last reviewed: 2017-06-05
Last modified: 2016-06-01
Last reviewed: 2017-06-05
This content is reviewed periodically and is subject to change as new health information becomes available. The information is intended to inform and educate and is not a replacement for medical evaluation, advice, diagnosis or treatment by a healthcare professional.
Copyright ©1986-2018 Barton D. Schmitt, MD FAAP. All rights reserved.